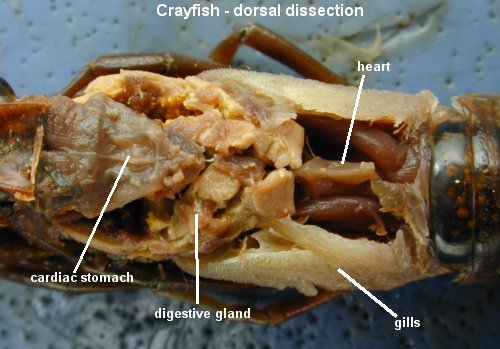
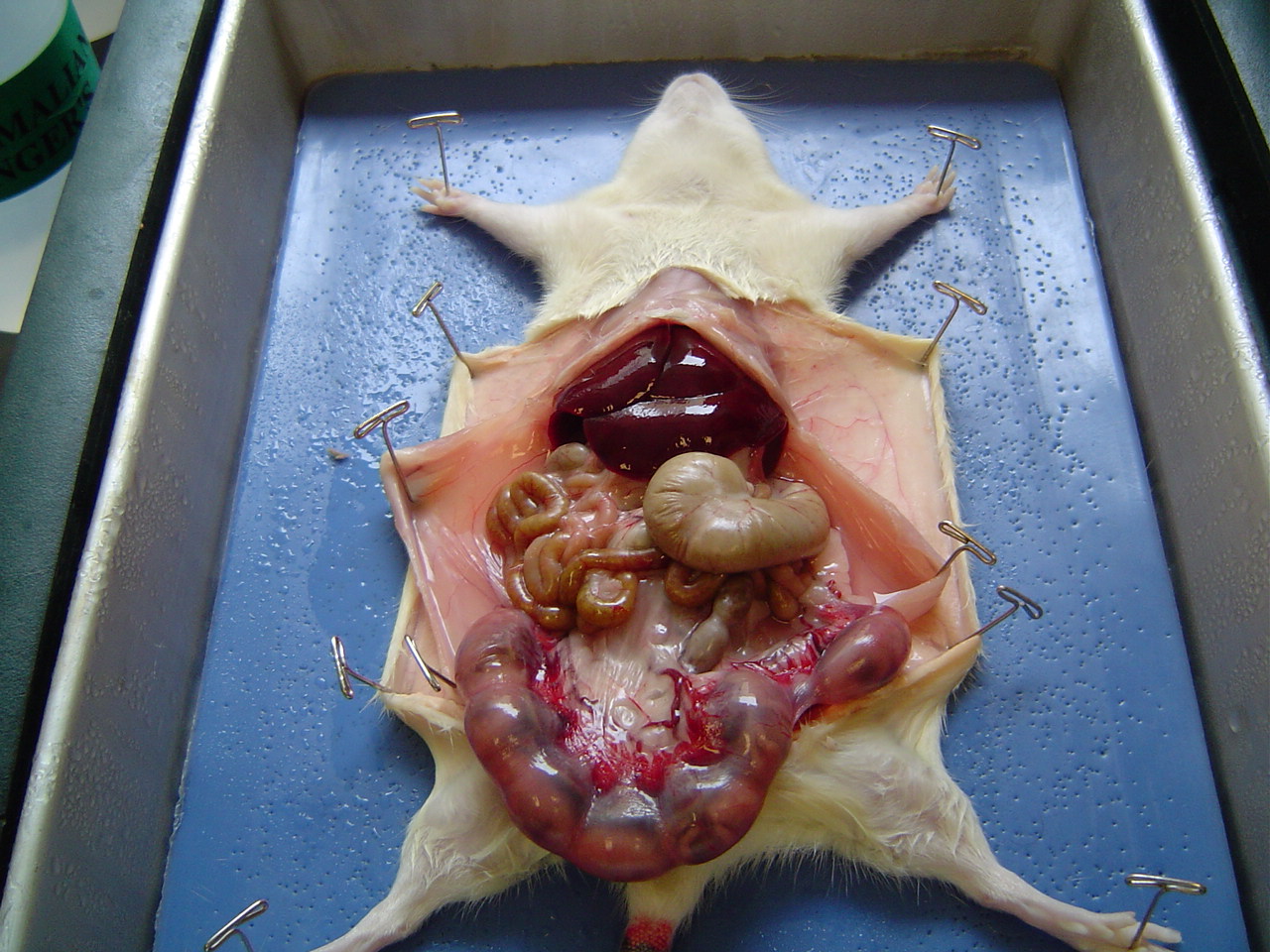
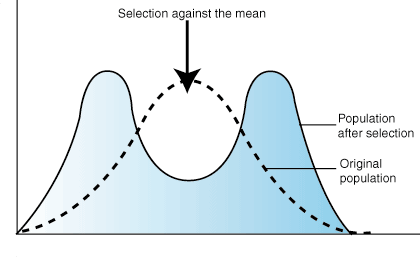
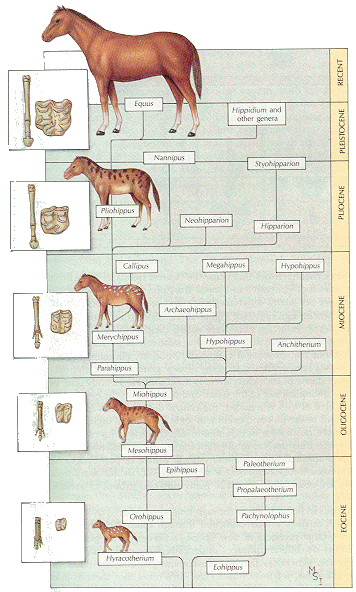
- Grasshopper
2. Frog
- Similarities
-Both have a set of jumping legs.
- Differences
-Grasshopper has an exoskeleton, frog has endoskeleton.
-Grasshopper has wings, frog doesn't.
-Grasshopper has a compound eye, frog has a normal eye.